832) 660 4838
281) 727 6582
We all understand that the brain is an essential component of the human body. It is the central control hub for all our bodily function, so if it is in crisis, the effects can be devastating. Under the umbrella of brain diseases, there are many individual variations, all vary widely depending on the particular condition. Brain diseases can result in other comorbid conditions such as paralysis, seizures, and comas.
1. Meningitis
Meningitis is the inflammation of the lining that surrounds the brain and the spinal cord. Usually due to infection, bacterial and viral meningitis are the two most common forms of the disease. However, other cases are known to be caused by fungi, chemical irritations, drug allergies, and some cancers. The inflammation can be deadly serious if left untreated and complication can occur such as seizures, brain damage, and hearing loss. Symptoms can vary depending on age and the type of meningitis, but hospitalization is the most immediate action in these cases as early diagnosis can prevent further complications.
2. Encephalitis
Where meningitis is the inflammation of the membranes that line the skull, Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain itself. The brain tissue becomes inflamed as the result of the body fighting off a viral infection, or sometimes the immune system will attack the brain tissue by mistake. This condition is acute and requires immediate medical attention. After experiencing some fever and headache, further increasing symptoms include seizures and loss of consciousness, drowsiness, and confusion. It can also lead to a coma. Direct infection of the spinal cord and brain is known as primary encephalitis, and an infection that started elsewhere and spread to the brain is known as secondary encephalitis.
3. Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease was eventually named after an English physician named James Parkinson. This neurodegenerative disease affects the nerves in the central brain area. The nerves degenerate slowly because the brain stops producing dopamine, a neurotransmitter. Without his, a person cannot control their body and emotions accurately. People can live with Parkinson's symptoms for years. It causes problems over time such as shaking hands, movement and coordination difficulties, stiffness in the limbs and unstable posture and slowness to move about. There is no cure but treatment to make life more comfortable.
4. Brain abscess
A brain abscess can form a few different ways. On a relatively healthy person (no other bodily infections or wounds), a weakened immune system can cause a bacterial infection in the brain. Pus and dead cells form because the system isn't working properly, thus causing the infection and abscess. It also occurs when a virus, bacteria or fungi reach the brain remotely, via an already established problem. The bacteria can travel to the brain through an infection somewhere else in the body, such as heart or lung infections, sinus infections, and problems or even serious tooth problems.
5. Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease
Dementia and Alzheimer's disease are similar, but not the same thing, as they are often mistaken to be. Alzheimer's is a form of Dementia. With Dementia, there is a decline in cognitive function. This is due to death, damage or malfunction of brain cells brought on by strokes, alcohol abuse, and other conditions. Alzheimer's Disease kills and destroys brain cells. They begin to degenerate or form an abnormal tissue build up. This causes progressive memory loss and changes in behavior and personality. These conditions are a combination of genetics, lifestyle, and environment , but it is not entirely clear exactly what causes it.
6. Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a seizure disorder and is one of the most common neurological disorders in the world. Its main trait is unpredictable seizures that range in severity, but they can cause many other health problems as well. A seizure is the disruption of any electrical communication between neurons in the brain. Epilepsy is a chronic noncommunicable disorder of the brain. To diagnose epilepsy, a person must experience two or more unprovoked seizures, separated by at least 24 hours.
7. Stroke
Stroke is a bleeding on the brain. This bleeding then causes blood flow and oxygen to slow or stop, and this affects the body part connected to that area of the brain. There are many different kinds of stroke, caused by variants of blockages such as a clot, an aneurysm, hematoma, or cerebral edema. This kind of brain disease is a vascular condition, which deals with blood vessels in particular.
8. Brain tumor
A brain tumor any mass of abnormal tissue cells, which form a growth inside the brain. These growths can be benign (non-harmful) or malignant (cancerous). Either way, they can cause problems by the pressure they cause onto the brain. Tumors grow because more and more cells combine into the mass. As it grows in size, the risk of seizure, motor function disruption and confusion grows. Doctors can treat cancerous tumors or remove them depending on location and size. Treatment is not always required in the case of benign tumors, unlike cancerous tumors, they will not spread to other parts of the body.
9. Autoimmune conditions
There are specific brain diseases, which is linked to an autoimmune condition. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is when the immune system damages the body's nerves; it attacks them by mistake. This causes fatigue, weakness and muscle spasms, occurring periodically or becoming progressively steadier as time goes by. Vasculitis is also linked to brain disease - this is an inflammation of blood vessels of the brain. Vasculitis causes headaches and seizures, confusion and unconsciousness.
10. Lou Gehrig's Disease
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is the medical name of Lou Gehrig's disease. The name of this diseases refers to Lou Gehrig who was a famous baseball player in the 1930's. Gehrig suffered from muscle atrophy. Lou Gehrig's disease is a neurodegenerative disease, which affects the brain and spinal cord, specifically the sections of nerve cells, which signal and controls muscles. The motor neurons die, and the nerve area scars or hardens, which is where sclerosis comes from. Sporadic ALS is the most common form of the disease with up to 90% of cases diagnosed, and familial ALS, which counts for 5-10%.
RedAcu.Com
Promoting Self-Healing
[ URGENT CARE ]
Nutrition for children's brain development
At the age of the children is essential nutrients necessary for brain growth and development. Nutrition helps in brain intelligence in children, food is one of the most important and influential elements of brain development in children because food contains essential nutrients needed by the brain such as vitamins, minerals, glucose, protein, and essential fats.
Glucose is the most important source of energy for the brain, the brain requires glucose to work while glucose is the smallest form of carbohydrates we normally get in staples such as rice, corn, potatoes and so on.
The supporting elements of the brain's work are the amino acids and fatty acids in sufficient quantities, the two elements forming new tissue or forming a nerve sheath. The amino acids obtained from the meal contained proteins therein and the fatty acids derived from fat-containing foods.
There are 2 types of fat that are bad fat and good fat, we always think that fat can be dangerous, but still, there is fat which is positive, good fat very much needed body about 60% for brain formation.
Various nutrients are needed for brain development in sufficient quantities, meaning not too much or not too little. A number of nutrients in the brain will affect the work of the brain that makes the nervous system is not normal
Food For Brain Nutrition
The brain also works like other organs in the body so it requires adequate nutrition. in the childhood of the brain is in the process of development and requires a good intake of nutrients for the intelligence of children, intake of such nutrition in the can of food
1. Wheat, has a carbohydrate content with a low glycemic index. The ability of the brain to concentrate and focus on a thought it can be of sufficient energy
2. Fish, has the essential fatty acid content needed by the brain, the type of fatty acid needed by the brain that is omega-3 and omega-6
3. Seed, also has a fatty acid content, intake of fatty acids that will not be balanced disrupted brain work processes.
4. Eggs, is a source of protein that contains vitamin B complex (B6 and B12) in addition to the eggs also contain omega-3.
5. Broccoli, a source of vitamin K, this vitamin is used to strengthen the brain and support the function of knowledge (cognitive)
And many other foods are also very needed for brain development in children, namely foods that contain minerals and iron, the content can be on the meat, beans, and rice.
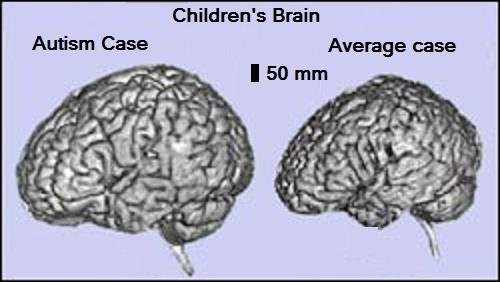
How inflammation and gut bacteria influence autism
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) affect 1 in 68 children in the United States.
A new study investigates the relationship between autism, the immune system, gastrointestinal issues, and gut bacteria. The story is a complex one with many questions still remaining unanswered, but this latest project adds insight.
A new study examines the communication lines between gut and brain.
Characterized by difficulties with socializing, and often accompanied by repetitive behaviors, this neurodevelopmental disorder harbors many mysteries.
Despite its prevalence and a glut of research, the causes behind ASD are still not fully understood.
Although ASD primarily impacts the brain, over recent years, links with other systems have become clear — in particular, gastrointestinal (GI) issues seem to occur more often in individuals with ASD than in the rest of the population.
In one study, compared with typically developing (TD) children, those with ASD were six to eight times more likely to report GI symptoms such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
Other studies have shown that children with ASD who experience GI problems are more likely to have more severe symptoms of ASD. Also, treating the GI symptoms can sometimes relieve the behavioral and social symptoms of ASD.
Interestingly, behavioral issues are found alongside other conditions that impact the gut. For instance, people with celiac disease are more likely to have autism-like traits and other psychological symptoms. The gut and behavior seem tied together in some way.
According to many researchers, the GI issues that come with ASD might be due to two factors: firstly, inappropriate immune activation, causing inflammation of the tract; and, secondly, differences in the types of gut bacteria that are present.
" There is nothing to compare with your health. "
25222 Grogan's Mill Road, The Woodlands, Texas 77380
www.RedAcu.com
TEXT OR CALL
832) 660 4838